Intro:
It is come the time to review the MUSHKIN PC8000! Let’s see how do they perform!
.jpg)
.jpg)
Specs:
1000MHz DDR2
CL 4-5-4-11
(CAS-TRCD-TRP-TRAS)
512MB and 1GB module
Unbuffered
Mushkin REDLINE 2x1gb XP2-8000 4-5-4-11
Lifetime Warranty
2.2-2.3 Volts
240 Pin DIMM
.jpg)
We can consider this memories as High-end ones, the one in the 2gb kits field that goes from 400€ to 500€.
The PCB is a classic Brain-power one with 6 ULNs, now used by most of the high-end memories brands.
.jpg)
While the chips mounted should be the Micron D9 since they react pretty fine in overclocking tests.
.jpg)
This kit is guaranteed byt Mushkin to work at 500MHz (1000 MHz DDR2), with tight timings (4-5-4-11), but as we will see from the tests these memories reach and break the 1000MHz wall with a lot tigher timings!
We are in front of a new type of heatspreader, longer in the top to make bigger the heating-surface, but it leaves some place to let the air come in and get the heat out of it. All this will make this heat-spreader a very good one, since with 2.4v this kits seem pretty cold.
These memories seems to offer high performances, they seems to be very good for best video-gamers who doesn’t want to lose not even a single frame, or for the benchmarks lovers, always looking for more and more frames in the 3Dmark, or looking to lower their S-pi time!
.jpg)
.jpg)
TESTING PLATFORM:
Intel P4 631 cooled by Zalman 7000-b Cu
Asus P5WD2-E premium 975X
Mushkin REDLINE 2x1gb XP2-8000 4-5-4-11
OCZ 520
ATI X1300
S.O. Windows 2003 server
Software: S-pi 1.4 Mod.
All the tests where made with two different voltage tensions:
=> 2.25v: to simulate the daily-use
=> 2.40v: to simulate the benchmark test, and to analyse the behaviour of this memories with the gain of volts.
For the Super-Pi tests were made two of them: 1MB to find the last MHz, and 32MB.
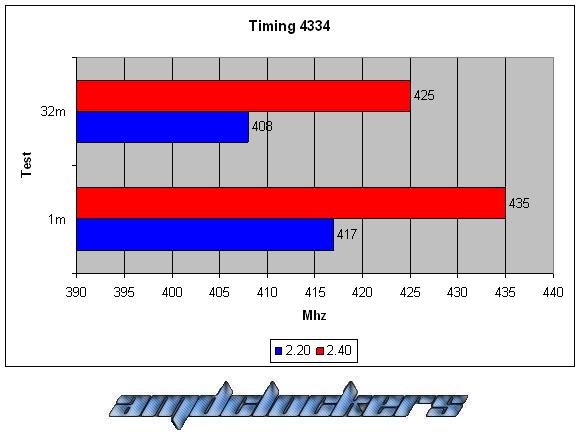
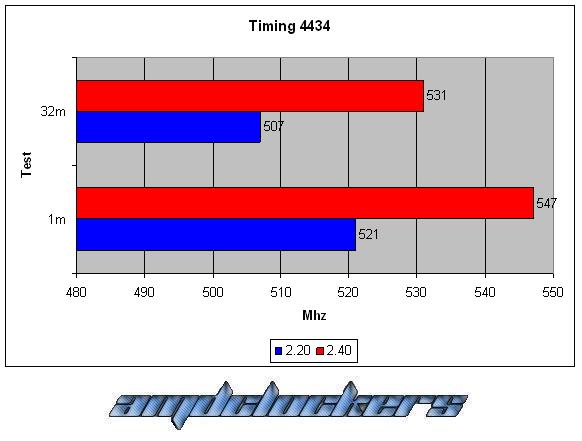
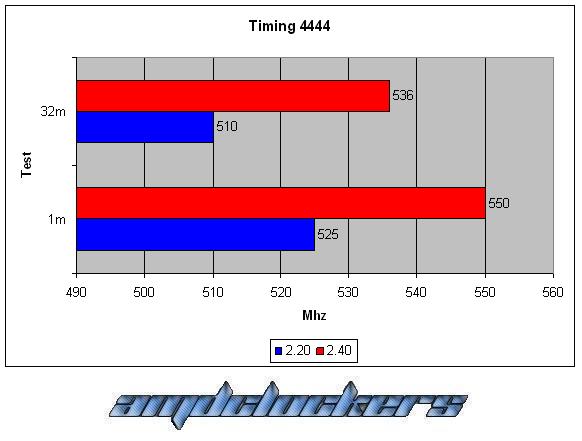
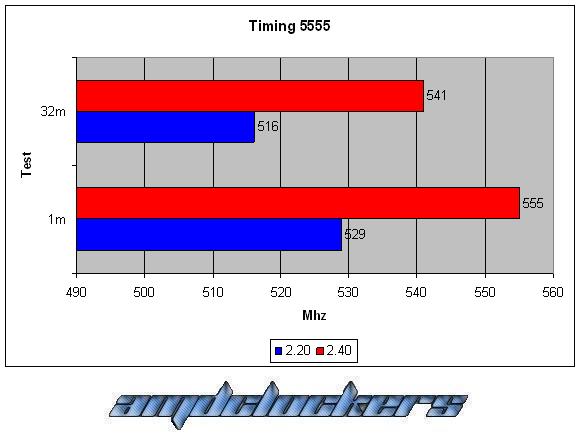
Looking at the Timings that we can change (generally from the Advanced Chipset Features menu in the motherboards bios), just four of them are the ones more used:
· CAS Latency (Tcl): refers to the length of time, in clock cycles, it takes for a request sent from the memory controller to read a memory location and send it to the module's output pins. Lower values means higher performance. Obviously a Cas 3 implies different performance if the memory works at 166MHz or 200MHz!
· RAS to CAS Delay (Trcd): the dates in the memories moduleds are disposed and read in raw and column, starting from the firsts lines and then from the columns. The TRCD means the delay in clock cycles between the RAS signal and the CAS one. Lower values means higher performances.
· RAS Pre-charge Time (Trp): this value refers to the length of time, in clock cycles, between a RAS command the the next one. In this length of time the condensators of the memories are pre-charged. This operation is indispensable for the DRAM characteristic we told before. Obviously lower values means higher performances.
· Cycle Time (Tras): refers to the length of time, in clock cycles, it takes to capture the date from the memory and making it avaible for the output. Lower values means higher performance.
The timings were set up by bios are in this order:
CAS-TRCD-TRP-TRAS.
This CPU has the multiplier locked, so we had to works in a-synchronised mode to test the stability at high frequencies: we used the 4/5, 3/5, 2/3 and ½ divisors
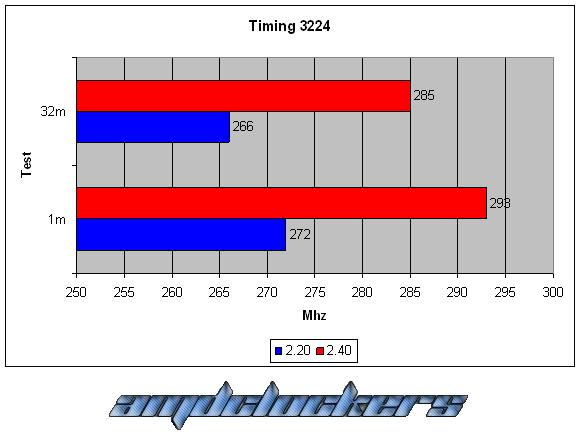
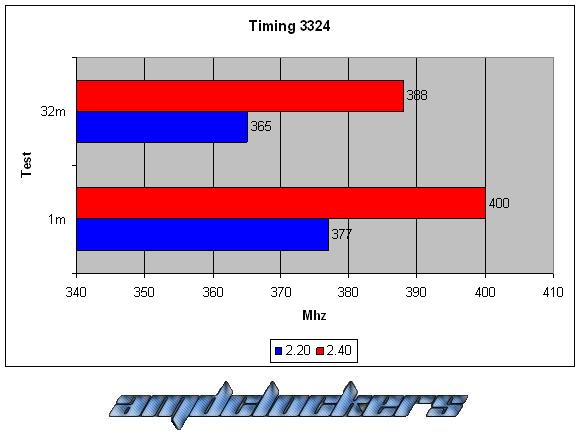
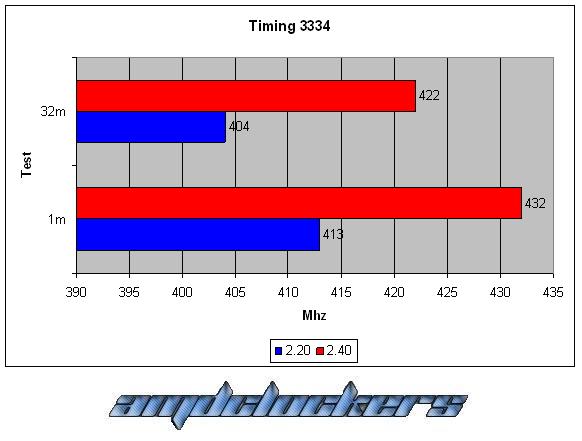
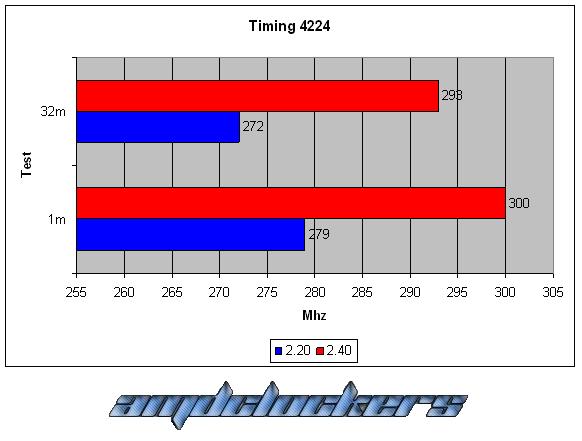
CONCLUSIONS:
As we can see this kit react very good with a voltage gain, we have a 10% better performance at least both in the 1M S-pi and in the 32M S-pi. This kit could reach 555MHz at most, awesome performances! But over DDR2 1110 we couldn’t go in windows, even with cas 5, we have reached the physical limit of this chip. This memories are caracterized by their awesome performances and by their fabulous heat-spreader!
Overall score:

Thanks Mushkin and Sirius Computer


By Andrea De Angeli & Marco Dominici


